No matter what the number of subscribers and application scope, mobile payment service has been mature in Japan, South Korea and Europe. With aggressive promotion of 3G services in China, mobile payment service has evolved from its infancy into growth period. In 2009, the number of mobile payment users worldwide registered 108 million with a rise of 25.6% from a year earlier, and it is expected that the number will be 147 million in 2010.
Given the enormous potentials of mobile payment market, ResearchInChina and www.1diaocha.com cooperated to conduct a survey on mobile payment network in August 2010. In the survey, there were 600 respondents most of whom were at the age of 20-50, men accounted for 50.7% and women 49.3%. The survey mainly covered Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing, Guangzhou, Chengdu and other 18 cities. The respondents were national civil servants, teachers, military personnel, corporate executives, general staff, sole proprietors, blue-collar workers and students, with the monthly income ranging from RMB2000 to RMB20,000.
In regard to the reason for not using mobile payment, according to the result of the survey,68.9% of the respondents worried about security. Security was the issue that consumers were most concerned about. 36.2% of the surveyed said they did not know well about mobile payment, 22.3% felt that it was inconvenient to subscribe mobile payment service, 17.9% thought that it was not easy to operate, 16.0% said their mobile phones did not support the function, 14.2% thought that the cost was high. Therefore, the promotion of mobile payment should base on good security measures which can resolve potential safety problems, excellent publicity, and simplified mobile payment methods which make subscribers experience the convenience of mobile payment.
Reasons for Subscribers Not Using Mobile Payment 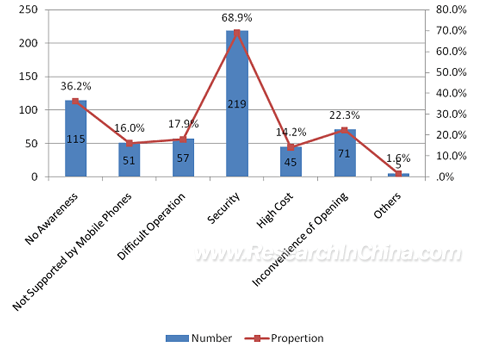
Source: ResearchInChina; www.1diaocha.com
In respect of subscription methods of mobile payment acceptable to subscribers, according to the result of the survey, 58.2% of the respondents preferred to subscribe the service in banks, 20.4% would like buy SD cards or mounting, 15.1% changed SIM cards, and only 6.3% wanted to replace cell phones. It can be drawn from above that subscribers prefer the most convenient method. On the other hand, the low-to-high proportion represents the cost from the high to the low. Subscribers are unwilling to pay additional cost when they subscribe mobile payment service. This shows that NFC mobile phones with mobile payment function are the cell phones that subscribers dislike most when they wish to subscribe mobile payment service. But now, consumers replace their cell phones frequently. If having been implanted with NFC feature at factories, there will be a certain market space for subscribing mobile payment service by changing phones.
Subscription Methods of Mobile Payment that Subscribers Can Accept 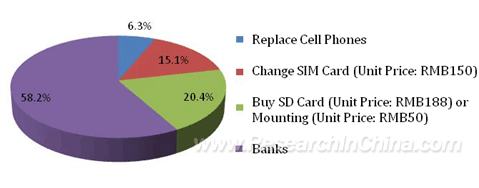
Source: ResearchInChina; www.1diaocha.com
Concerning the implementation methods of mobile payment, according to the result of the survey, 51.4% of the respondents rendered SMS, 29.8% dialed calls and 15.2% paid in short distance. This result is closely related with the small population of POS machines at present initial stage. With the maturity of mobile payment in the future, the number of POS machine will increase, and it is expected that short-distance payment will take a large percentage.
Mobile Payment Methods 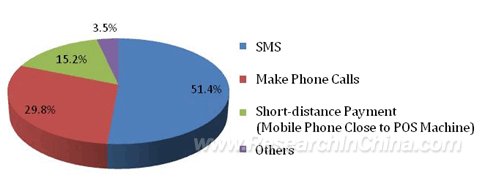
Source: ResearchInChina; www.1diaocha.com