近年来,随着电动汽车市场的快速发展,中国市场涌现了上百家新兴造车企业,有一定知名度大约有50家。在经济大环境低迷,汽车销量走低的大背景下,多数新兴造车企业的发展将受挫,资本和产业资源将向少数领先的新兴造车企业倾斜。
《2018年中国新兴造车企业布局及智能网联功能对比分析报告》选取了其中比较有实力的19家新兴造车企业,研究其生产、研发、制造、销售、出行等布局,代表车型的智能化、网联化等配置对比,技术路线、发展战略等,全方位展示中国新兴造车行业的发展现状和趋势。
过去两年,新兴造车企业的融资并未放缓,领先企业从亿元级融资,逐步进入当前的十亿级,和接下来的百亿级。
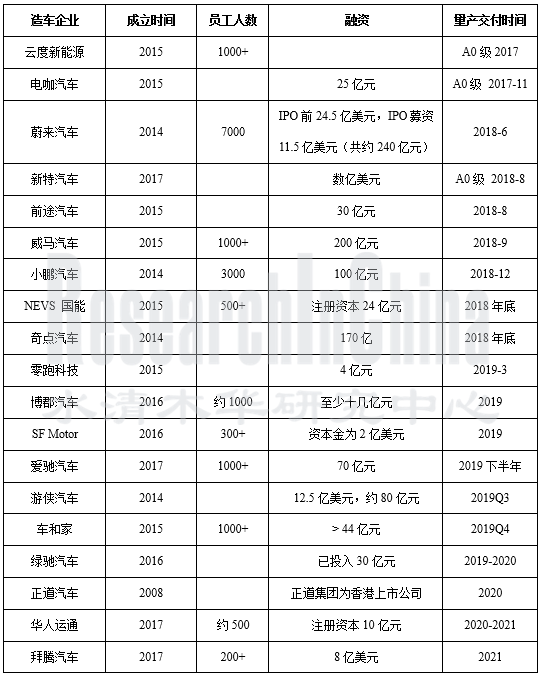
这19家企业从2018年起,多数进入产品量产上市阶段。2017年已经上市的云度新能源和电咖汽车车型,属于A0级。2018年已经和即将量产交付的有7家,2019年有6家,2020-2021年有4家。
得益于更多资本的进入,以及汽车行业处于智能化、网联化、电动化、共享化的大变革时期,新兴造车企业通过差异化竞争,依靠领先Tier1的支持,利用本土化创新,试图在庞大的中国汽车市场上寻得一席之地。
采用最前沿的汽车电子电气架构,增加智能化网联化配置,配上本土化的特色服务(如快递到后备箱)是多数新兴造车者的选择。佐思产研细化出110项智能化网联化功能,并以此评价19家企业代表车型的智能网联化程度,计算出得分。
简单总结一下新兴造车企业的智能网联化策略和趋势:
一、更多采用液晶屏,往往会采用4-6屏。多屏成为一个亮点,也成为一个挑战。因为多屏显示和互动,都需要耗费大量的计算资源,势必推高芯片成本和软件开发成本。

二、更多的采用HUD、多种交互系统、生物识别系统,为副驾和后座乘客提供独立的娱乐和交互空间。
三、预置二十多个环境感知传感器,为ADAS和自动驾驶功能升级做硬件准备。譬如蔚来ES8搭载21个传感器,小鹏G3搭载25个,奇点iS6也搭载25个。部分厂商甚至表示用户购车后,传感器等硬件还可以升级。因为软件升级的需要,OTA成为标配。
四、由于国内供应商缺乏成熟可落地的自动驾驶解决方案,新兴造车企业在自动驾驶方案上,有的选择Mobileye方案,有的选择自行开发迭代。蔚来汽车、威马汽车、游侠汽车都选择与Mobileye合作。不选择重量级供应商,自行开发(或者与小伙伴一起开发)车联网和自动驾驶系统的风险在于,在WAYMO、特斯拉等对手已经遥遥领先的情况下,留给国内新兴造车者的时间不多。Mobileye方案、斑马智行系统、百度Apollo系统正在被越来越多的车企采用。
五、设立专项资金,投资和支持自身的供应链体系。如蔚来汽车的蔚来资本,融资目标是100亿元人民币,已经通过人民币基金投资了共享汽车、无人驾驶、汽车新材料领域的15家企业。电咖汽车产业发展基金管理基金规模将超25亿,将专注于智能电动汽车相关产业链的投资,在新能源动力技术、智能驾驶、共享服务等方面整合资源。奇点汽车与苏州政府合作成立100亿元的智能电动汽车产业投资基金。
总体上讲,新兴造车企业的涌现,为中国汽车产业的创新和变革带来了活力。数目众多本土车企的存在,为智能网联汽车产业链的传感器、软件和算法、通讯系统、控制器、芯片、联网系统、系统集成、出行服务、娱乐服务、泊车服务、充电系统等供应商带来了诸多发展机遇,使得中国成为智能网联汽车领域创业企业最多,创新速度最快的国家。
特斯拉在2018年第三季度取得了重大的成功, 以特斯拉为榜样的数十家中国新兴造车企业,也将会有几家能够脱颖而出。
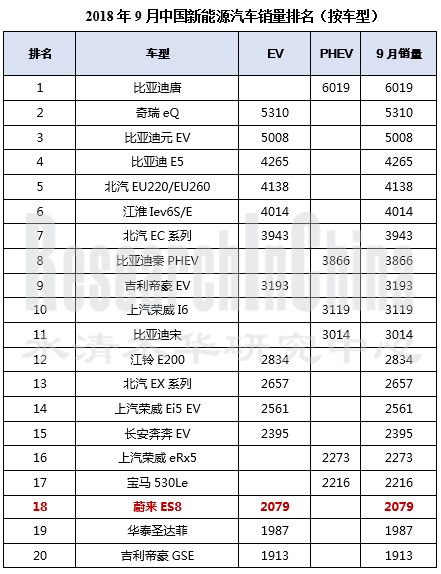
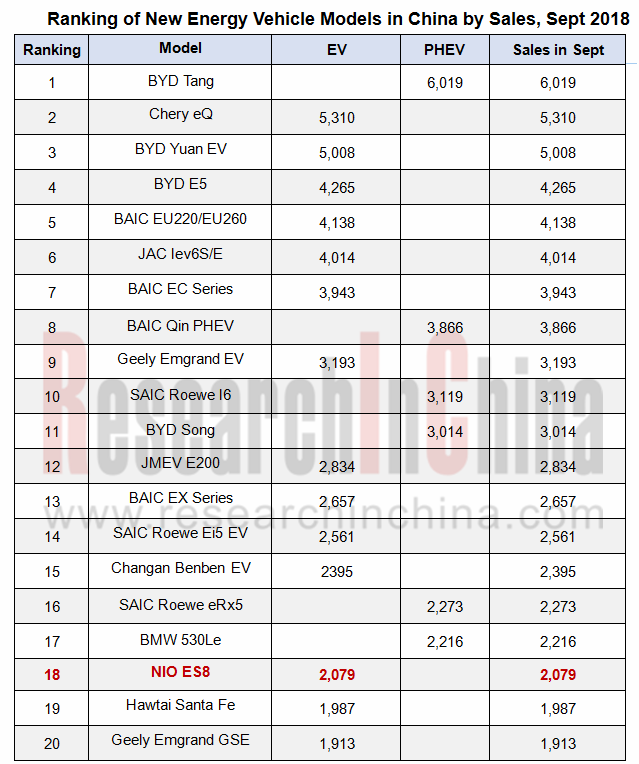
从9月的中国新能源汽车销量排名来看,蔚来ES8已经挤进了前20。明年下半年,将会有更多新兴造车企业的车型上榜。
There have emerged more than a hundred new automakers in the wake of the rapidly expanding electric vehicle market in China over the past few years, among which fifty ones or so have gained popularity. Amid the depressed economy and the waning vehicle sales, the majority of these players will suffer a setback in attempts to expand, and capital and industrial resources will thus flow to a few big ones.
19 emerging automakers are analytically selected in the report focusing on their layout in production, research and development, manufacturing, marketing and mobility, as well as configurations of their typical connected vehicle models, technology roadmaps and development strategies.
Emerging automakers did not yet slow their pace of raising funds in the past two years. Bellwethers’ financing scale jumped from more than hundreds of millions of yuan to billions of yuan before hitting tens of billions of yuan in the near future.
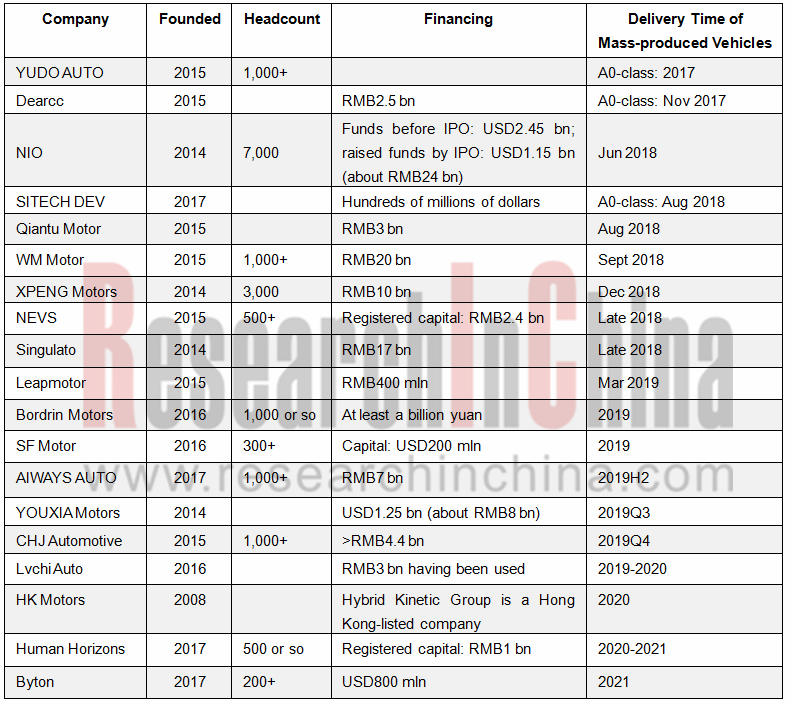
Most of the 19 firms have launched cars on the market since 2018. The vehicles released by YUDO Auto and Dearcc in 2017 are A0-class models. In 2018 another 7 automakers have cars delivered or to be delivered; in 2019, 6 carmakers will have launches; between 2020 and 2021, four carmakers will do so.
Emerging automakers strive for a place in the huge Chinese automobile market where they compete in a differentiated way with the help of Tier1 suppliers. Thanks to more capital inflows, they can exert themselves to innovations in local Chinese market as automobile is going smart, connected, electrified and shared.
Most players use the cutting-edge automotive electrical/electronic architecture, coupling local featured services (e.g., allowing couriers to put a package directly into the receiver’s car trunk), to build intelligent connected cars. The report introduces 110 intelligent and connectivity capabilities as a points-based criterion system to evaluate how typical car models of the 19 firms are intelligent and connected.
Here is a briefing of connected car strategies and development directions of emerging automakers:
1. These firms prefer 4-to-6-inch LCD screens. Multi-screen is a highlight but also a challenge, because display and interaction of multiple screens cost a lot of computing resources, which undoubtedly leads to the rising costs of chip and software development.
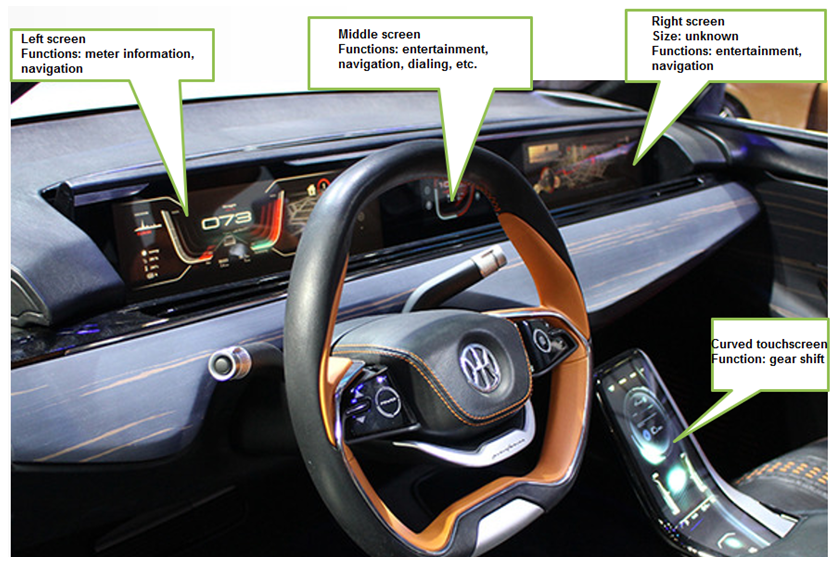
2. More use of HUD, multiple interactive systems and biometric system provides front and rear seat occupants with independent space of entertainment and interaction.
3. More than 20 sensors are preset as hardware for upgrading ADAS and automated driving functions. Examples include NIO ES8 equipped with 21 sensors, Xpeng G3 with 25 and Singulato iS6 with 25. Some manufacturers even express that users can get an upgrade of hardware like sensors. OTA has been a standard configuration for software update.
4. For Chinese suppliers have no mature applicable automated driving solutions, the emerging automakers choose either Mobileye’s solutions or independent development and iterations, of which NIO, WM Motor and YOUXIA Motors partner with Mobileye. Those without cooperating with major suppliers are running out of time to develop telematics and automated driving systems by themselves (or teaming up with their partners), because their foreign counterparts like WAYMO and Tesla have left them far behind. Mobileye’s solutions, Banma Zhixing system and Baidu Apollo system are being utilized by more and more automakers.
5. These players set up special funds to back their own supply chain system. For example, NIO Capital, NIO’s fund management agency with fundraising target of RMB10 billion, has invested 15 companies in the areas of car sharing, autonomous driving and automotive new materials through its RMB funds; Dearcc’s automotive industry development funds managing more than RMB2.5 billion, will concentrate on investment in the industry chain of intelligent electric vehicle and integration of resources in new energy power technology, intelligent driving and shared services; Singulato and Suzhou Municipal Government have built a RMB10 billion joint investment fund for intelligent electric vehicle industry.
As a whole, the boom of emerging automakers lends vigor to innovation and transformation in China’s automobile industry. A great number of Chinese automakers offer opportunities for suppliers in the intelligent connected vehicle (ICV) industry chain covering sensors, software and algorithms, communication systems, controllers, chips, connectivity systems and system integration, mobility services, entertainment services, parking services and charging systems, making China the one boasting the most number of start-ups in the ICV field and innovating at the fastest speed.
Tesla achieved great success in the third quarter of 2018. It is believed that several out of dozens of Chinese emerging automakers will come to the fore.
NIO ES8 has edged into the top20, according to the ranking list of new energy vehicle models in China by sales in September 2018. The emerging automakers will have more models on the list in the second half of 2019.
1. 新兴造车行业总体情况
1.1 中国新兴造车企业汇总(约50家)
1.2 获得资质的新能源电动车企业
1.3 新兴造车企业制造基地分布
1.4 新兴造车企业可靠度排名
1.5 新兴造车企业综合对比(包括成立时间、融资规模、核心团队、员工人数、总部所在地、工厂所在地、规划产能、首款量产车型、车型定位、车型定价、上市时间、生产制造合作、续航里程、车联网合作情况、自动驾驶合作情况、充换电措施、出行布局等。)
2. 车联网和自动驾驶功能对比
2.1 新兴造车车型的控制方式对比(含触摸/语音/手势/远程)
2.2 新兴造车车型的显示模块对比(含仪表/中控/HUD/后排娱乐等)
2.3 新兴造车车型的外设和智能照明功能对比
2.4 新兴造车车型的传感器配置对比
2.5 新兴造车车型的ADAS功能对比
2.6 新兴造车企业的自动驾驶布局对比
2.7 新兴造车车型的通讯和联网功能对比
2.8 新兴造车车型的其他智能网联化功能对比
2.9 新兴造车车型的系统和架构对比
3. 新兴造车典型车型座舱功能图解
3.1 蔚来ES8座舱功能图解
3.2 威马汽车EX5座舱功能图解
3.3 拜腾BYTON Concept座舱功能图解
3.4 爱驰U5 ION座舱功能图解
3.5 前途汽车K50座舱功能图解
3.6 奇点汽车iS6座舱功能图解
3.7 正道汽车K350座舱功能图解
3.8 正道汽车H500座舱功能图解
3.9 云度π7座舱功能图解
3.10 新特DEV1座舱功能图解
4. 代表车型智能网联功能及得分
4.1 蔚来ES8智能网联功能列表及得分
4.2 威马EX5智能网联功能列表及得分
4.3 前途K50智能网联功能列表及得分
4.4 奇点iS6智能网联功能列表及得分
4.5 云度智能网联功能列表及得分
4.6 理想制造One智能网联功能列表及得分
4.7 小鹏G3智能网联功能列表及得分
4.8 零跑S01智能网联功能列表及得分
4.9 爱驰U5 ION智能网联功能列表及得分
4.10 NEVS 9-3EV智能网联功能列表及得分
4.11 游侠X智能网联功能列表及得分
5. 新兴造车汽车企业研究
5.1 蔚来汽车
5.1.1 蔚来汽车简介
5.1.2 蔚来汽车核心管理团队
5.1.3 蔚来汽车融资历程
5.1.4 蔚来汽车发展历程
5.1.5 蔚来汽车产品路线
5.1.6 蔚来汽车ES8与同类车型性能对比
5.1.7 ES8与同类车型的价格优势
5.1.8 蔚来汽车市场及商业模式
5.1.9 蔚来汽车在中国市场定位
5.1.10 蔚来公司全球战略合作伙伴
5.1.11 蔚来公司布局
5.1.12 蔚来总部和研发基地
5.1.13 蔚来生产基地
5.1.14 与其他主机厂的合作
5.1.15 IPO报告透露信息
5.1.16 蔚来辅助驾驶系统NIO Pilot
5.1.17 蔚来自动驾驶布局
5.2 小鹏汽车
5.2.1 小鹏汽车简介
5.2.2 团队构成和管理团队
5.2.3 全球生产研发布局
5.2.4 工厂和生产计划
5.2.5 小鹏汽车的充电站规划
5.2.6 小鹏汽车融资情况
5.2.7 小鹏汽车的智能网联化布局
5.3 威马汽车
5.3.1 威马汽车简介
5.3.2 创始团队和管理团队
5.3.3 融资概况
5.3.4 威马汽车发展历程
5.3.5 威马汽车产品战略
5.3.6 威马代表车型的智能网联配置
5.3.7 威马车型EX6和Isdera Commendatore GT
5.3.8 威马汽车商业模式创新
5.3.9 威马汽车四大研发中心和两大生产基地
5.3.10 威马汽车布局:生产制造、产品、出行
5.4 车和家
5.4.1 车和家简介
5.4.2 创始团队和管理团队
5.4.3 融资概况
5.4.4 车和家的发展历程
5.4.5 车和家的自动驾驶策略
5.4.6 车和家自动战略布局和规划
5.4.7 车和家计划在重庆的布局
5.4.8 车和家全球布局
5.4.9 车和家业务布局:生产制造、产品、出行
5.4.10 理想智造
5.5 奇点汽车
5.5.1 奇点汽车简介
5.5.2研发生产布局
5.5.3首款智能电动量产车型
5.5.4 iS6电子电器架构
5.5.5 娱乐域的双主干网架构
5.5.6 iS6传感器系统配置及实现功能
5.5.7 iS6主要供应商
5.5.8 奇点汽车营销体系
5.6 游侠汽车
5.6.1 游侠汽车简介
5.6.2 游侠汽车融资情况
5.6.3 游侠汽车主要车型
5.6.4 游侠汽车生产基地
5.6.5 游侠汽车量产情况
5.6.6 游侠汽车合作伙伴
5.6.7成立欧洲研发中心
5.7 电咖汽车
5.7.1 电咖汽车简介
5.7.2 融资及生产基地
5.7.3 电咖汽车团队构成
5.7.4 电咖汽车EV10
5.7.5 电咖汽车ENOVATE
5.7.6 电咖汽车的智能网联布局
5.7.7 电咖汽车生产、销售及售后布局
5.8 爱驰汽车
5.8.1 爱驰汽车简介
5.8.2 创始团队和管理团队
5.8.3 融资概况
5.8.4发展历程
5.8.5技术优势
5.8.6全球布局
5.8.7产品布局
5.8.8制造基地
5.8.9 爱驰汽车的智能化
5.9 前途汽车
5.9.1 前途汽车简介
5.9.2 前途汽车发展历程
5.9.3 前途K50
5.9.4 前途汽车三大平台新产品计划
5.9.5 前途汽车品牌体验店
5.10 国能汽车研究
5.10.1 NEVS (国能汽车)简介
5.10.2 NEVS生产基地及规划
5.10.3国能新能源与NEVS 9-3EV
5.10.4 InMotion概念车
5.10.5 NEVS 战略合作
5.11 云度新能源
5.11.1企业简介
5.11.2 代表产品
5.11.3产品价格及销量
5.11.4 云度·回购π计划
5.11.5 2018目标及规划
5.11.6总体定位及规划
5.12 博郡汽车
5.12.1 企业简介
5.12.2 核心团队
5.12.3 分公司结构
5.12.4 产品规划
5.12.5 合作伙伴
5.12.6 博郡汽车销售模式
5.13 华人运通研究
5.13.1 华人运通简介
5.13.2 创业团队
5.13.3 华人运通的发展历程
5.13.4 代表产品
5.13.5 多项前瞻性示范技术和项目持续落地
5.13.6 华人运通:生产制造、产品、及人才战略
5.13.7 华人运通战略—三大平台联接“车、路、城”
5.14 绿驰汽车
5.14.1 绿驰汽车简介
5.14.2 融资情况
5.14.3 产品平台及新车上市计划
5.14.4 车型组合
5.14.5 绿驰SUV
5.14.6 绿驰微型车
5.14.7 绿驰轿跑车
5.14.8 生产基地
5.14.9全球研发平台
5.14.10 绿驰智能网联技术规划
5.15 拜腾汽车
5.15.1 拜腾汽车简介
5.15.2 核心团队
5.15.3 融资情况
5.15.4 全球业务布局
5.15.5 工厂及建设进展
5.15.6 BYTON M-Byte车型
5.15.7 BYTON K-Byte车型
5.15.8 拜腾汽车合作进展
5.15.9 拜腾汽车发展计划
5.16 零跑汽车
5.16.1 零跑汽车简介
5.16.2 零跑汽车生产基地
5.16.3 新车计划
5.16.4 零跑汽车S01
5.16.5 零跑汽车S01自动驾驶技术发展图
5.16.6 零跑汽车T03和C11
5.16.7 零跑与大华联合研发AI自动驾驶芯片
5.16.8 零跑汽车的战略合作
5.16.9 “直营+城市合作伙伴”商业模式
5.17 新特汽车
5.17.1 新特汽车简介
5.17.2 发展历程
5.17.3 新特DEV1
5.17.4 新特DEV1参数
5.17.5 新特DEV1智能网联配置
5.17.6 新特汽车合作伙伴
5.17.7 新特汽车发展规划
5.17.8 新特汽车智能网联布局
5.18 正道汽车
5.18.1 正道汽车简介
5.18.2 正道增程式电驱动汽车
5.18.3 正道汽车生产基地
5.18.4 正道主要汽车产品
5.18.5 正道汽车H600和K550
5.18.6 正道汽车K750
5.19 SF Motor
5.19.1 SF Motor 简介
5.19.2发展历程
5.19.3生产基地
5.19.4研发布局
5.19.5 两款SUV车型
5.19.6 首款量产车型
1. Overview of the Emerging Automakers in China
1.1 Chinese Emerging Automakers (about 50)
1.2 Qualified New Energy Electric Vehicle Companies
1.3 Manufacturing Base Distribution of Emerging Automakers
1.4 Ranking of Emerging Automakers by Reliability
1.5 Comprehensive Comparison between Emerging Automakers (time of establishment, financing, core teams, headcount, location of headquarters and factories, planned capacity, first production model, model positioning, model pricing, launch time, cooperation in manufacturing, mileage range, cooperation in telematics, autonomous driving, charging and swapping measures, mobility plans, etc.)
2. Comparison of Telematics and Autonomous Driving
2.1 Control Methods of Emerging Models (including touch / voice / gesture / remote)
2.2 Display Modules of Emerging Models (including instrument/center stack/HUD/rear seat entertainment, etc.)
2.3 Peripherals and Smart Lighting of Emerging Models
2.4 Sensor Configuration of Emerging Models
2.5 ADAS of Emerging Models
2.6 Autonomous Driving Layout of Emerging Automakers
2.7 Communication and Networking of Emerging Models
2.8 Other Intelligent Connection Features of Emerging Models
2.9 System and Architecture of Emerging Models
3. Cockpit Diagram of Emerging Models
3.1 Cockpit Diagram of NextEV ES8
3.2 Cockpit Diagram of WM EX5
3.3 Cockpit Diagram of BYTON Concept
3.4 Cockpit Diagram of AIWAYS U5 ION
3.5 Cockpit Diagram of Qiantu K50
3.6 Cockpit Diagram of Singulato iS6
3.7 Cockpit Diagram of HK Motors’ K350
3.8 Cockpit Diagram of HK Motors’ H500
3.9 Cockpit Diagram of Yudo π7
3.10 Cockpit Diagram of SITECH DEV1
4. Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of Typical Models
4.1 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of NextEV ES8
4.2 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of WM Motor EX5
4.3 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of Qiantu K50
4.4 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of Singulato iS6
4.5 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of Yudo
4.6 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of ONE
4.7 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of XPENG Motors G3
4.8 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of Leapmotor S01
4.9 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of AIWAYS U5 ION
4.10 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of NEVS 9-3EV
4.11 Intelligent Connected Functions and Ratings of Youxia X
5. Emerging Automakers
5.1 NextEV
5.1.1 Profile
5.1.2 Core Management Team
5.1.3 Financing
5.1.4 Development History
5.1.5 Product Route
5.1.6 Performance Comparison between ES8 and Similar Models
5.1.7 Price Advantage of ES8 over Similar Models
5.1.8 Market and Business Models
5.1.9 Positioning in the Chinese Market
5.1.10 Strategic Partners Worldwide
5.1.11 Corporate Layout
5.1.12 Headquarters and R&D Base
5.1.13 Manufacturing Base
5.1.14 Cooperation with Other OEMs
5.1.15 Information Disclosure of IPO Report
5.1.16 Driver Assistance System -- NIO Pilot
5.1.17 Autonomous Driving Layout
5.2 XPENG Motors
5.2.1 Profile
5.2.2 Team Composition and Management Team
5.2.3 Global Production and R&D Layout
5.2.4 Plants and Manufacturing Plan
5.2.5 Charging Station Planning
5.2.6 Financing
5.2.7 Layout in Intelligent Connectivity
5.3 WM Motor
5.3.1 Profile
5.3.2 Founding Team and Management Team
5.3.3 Financing
5.3.4 Development History
5.3.5 Product Strategy
5.3.6 Intelligent Connected Configuration of Typical Models
5.3.7 EX6 and Isdera Commendatore GT
5.3.8 Innovation of Business Model
5.3.9 Four R&D Centers and Two Manufacturing Bases
5.3.10 Layout: Manufacturing, Products, Mobility
5.4 CHJ Automotive
5.4.1 Profile
5.4.2 Founding Team and Management Team
5.4.3 Financing
5.4.4 Development History
5.4.5 Autonomous Driving Strategy
5.4.6 Strategic Layout and Planning for Autonomous Driving
5.4.7 Layout in Chongqing
5.4.8 Global Reach
5.4.9 Business Layout: Manufacturing, Products, Mobility
5.4.10 ONE
5.5 Singulato
5.5.1 Profile
5.5.2 R&D and Production Layout
5.5.3 The First Intelligent EV Production Model
5.5.4 Electronic and Electrical Architecture of iS6
5.5.5 Dual Backbone Network Architecture for Entertainment Domain
5.5.6 Sensor System Configuration and Functions of iS6
5.5.7 Main Suppliers for iS6
5.5.8 Marketing System
5.6 Youxia Motors
5.6.1 Profile
5.6.2 Financing
5.6.3 Key Models
5.6.4 Manufacturing Base
5.6.5 Mass Production
5.6.6 Partners
5.6.7 Establishment of Its European R&D Center
5.7 DEARCC
5.7.1 Profile
5.7.2 Financing & Production Base
5.7.3 Team Composition
5.7.4 EV10
5.7.5 ENOVATE
5.7.6 Layout in Intelligent Connected Field
5.7.7 Production, Sales and After-sale Layout
5.8 AIWAYS AUTO
5.8.1 Profile
5.8.2 Founding Team & Management Team
5.8.3 Financing
5.8.4 Development Course
5.8.5 Technical Superiority
5.8.6 Global Presence
5.8.7 Product Layout
5.8.8 Manufacturing Base
5.8.9 Intelligentization
5.9 Qiantu Motor
5.9.1 Profile
5.9.2 Development Course
5.9.3 K50
5.9.4 New Product Programs of Three Platforms
5.9.5 Brand Experience Shop
5.10 National Electric Vehicle Sweden (NEVS)
5.10.1 Profile
5.10.2 Manufacturing Base and Planning
5.10.3 NEVS 9-3EV
5.10.4 InMotion Concept
5.10.5 Strategic Partners
5.11 YUDO New Energy Automobile (YUDO AUTO)
5.11.1 Profile
5.11.2 Typical Product
5.11.3 Product Prices & Sales
5.11.4 YUDO•Buy-back π Program
5.11.5 Targets and Plans for 2018
5.11.6 Overall Positioning and Planning
5.12 Bordrin
5.12.1 Profile
5.12.2 Core Team
5.12.3 Structure of Branches
5.12.4 Product Planning
5.12.5 Partners
5.12.6 Sales Model
5.13 Human Horizons
5.13.1 Profile
5.13.2 Entrepreneurship Team
5.13.3 Development Course
5.13.4 Typical Product
5.13.5 Prospective Demo Technologies and Implementation of Projects
5.13.6 Strategies for Manufacturing, Products and Talents
5.13.7 The Strategy: Three Platforms Connect “Vehicle, Road and City”
5.14 LVCHI Auto
5.14.1 Profile
5.14.2 Financing
5.14.3 Product Platform & Plan for New Car Launches
5.14.4 Model Portfolios
5.14.5 LVCHI SUV
5.14.6 LVCHI Minicar
5.14.7 LVCHI Coupe
5.14.8 Manufacturing Base
5.14.9 Global R&D Platform
5.14.10 Planning of Intelligent Connected Technologies
5.15 BYTON
5.15.1 Profile
5.15.2 Core Team
5.15.3 Financing
5.15.4 Global Operations
5.15.5 Plants and Construction Progress
5.15.6 BYTON M-Byte Model
5.15.7 BYTON K-Byte Model
5.15.8 Progress of Cooperation
5.15.9 Development Plan
5.16 Leap Motor
5.16.1 Profile
5.16.2 Manufacturing Base
5.16.3 New Vehicle Plan
5.16.4 S01
5.16.5 Development Roadmap for S01 Autonomous Driving Technologies
5.16.6 T03 & C11
5.16.7 Leap Motor and Zhejiang Dahua Technology Co-develops AI Autonomous Vehicle Chip
5.16.8 Strategic Cooperation
5.16.9 “Regular Chain + City Partners” Business Model
5.17 SITECH DEV
5.17.1 Profile
5.17.2 Development Course
5.17.3 SITECH DEV1
5.17.4 Parameters SITECH DEV1
5.17.5 Intelligent Connected Configurations of SITECH DEV1
5.17.6 Partners
5.17.7 Development Plan
5.17.8 Layout in Intelligent Connectivity
5.18 Hybrid Kinetic Motors (HK Motors)
5.18.1 Profile
5.18.2 Extended-Range Electric Vehicle
5.18.3 Manufacturing Base
5.18.4 Key Automotive Products
5.18.5 H600 & K550
5.18.6 K750
5.19 SF Motor
5.19.1 Profile
5.19.2 Development Course
5.19.3 Manufacturing Base
5.19.4 R&D Layout
5.19.5 Two SUV Models
5.19.6 First Mass-produced Model